The human visual system is a marvel of biological engineering, allowing us to perceive the world around us with incredible detail and clarity. At the heart of this system lies the optic nerve, a crucial pathway that transmits visual information from the eyes to the brain. Understanding the intricate connection between the optic nerves and the brain is essential for comprehending how we see and interpret the world.
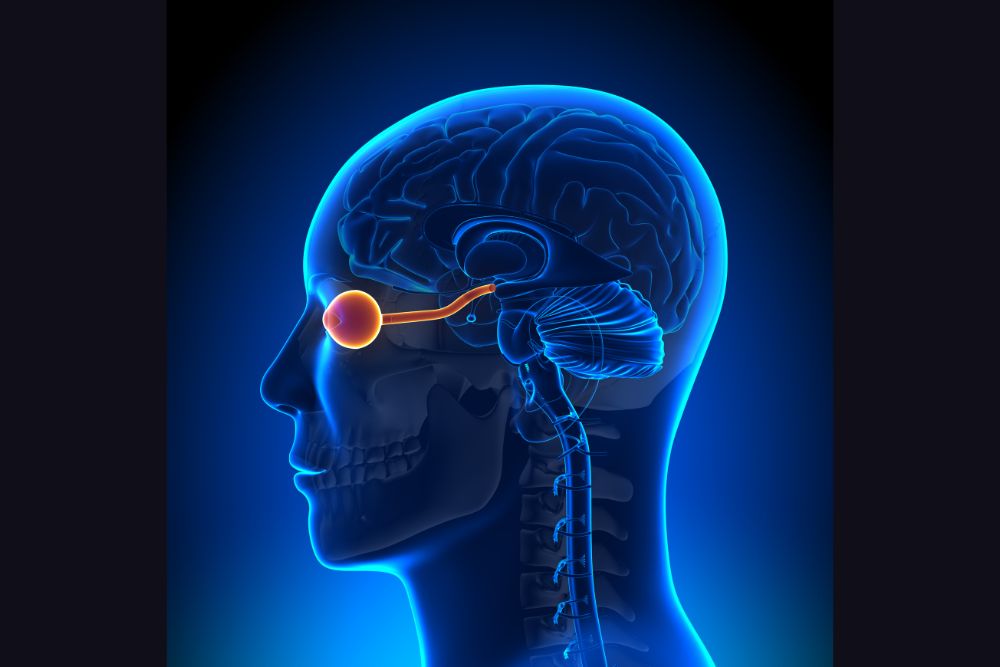
Anatomy of the Optic Nerve
The optic nerve, also known as cranial nerve II, is a bundle of approximately one million nerve fibers that originate from the retina of each eye. These fibers come together at the optic disc, also called the blind spot, where they form the optic nerve. The optic nerve exits the eye through the back of the orbit and travels toward the brain, carrying visual signals that are essential for vision.
Pathway to the Brain
After leaving the eye, the optic nerves follow a complex pathway to transmit visual information to various structures in the brain responsible for processing vision. The optic nerves initially converge at the optic chiasm, a point near the base of the brain where some fibers from each optic nerve cross over to the opposite side. This crossing of fibers allows for the integration of visual information from both eyes.

Once past the optic chiasm, the nerve fibers continue as the optic tracts, which project to different areas of the brain. The majority of fibers from the optic tracts terminate in the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) of the thalamus, a relay station for sensory information. From the LGN, visual signals are then transmitted to the primary visual cortex located in the occipital lobe of the brain, where they are further processed and interpreted.
Functional Significance
The connection between the optic nerves and the brain is crucial for several aspects of visual perception. By integrating visual information from both eyes, the brain can generate a coherent and three-dimensional representation of the surrounding environment. Additionally, the arrangement of nerve fibers within the optic nerves and tracts allows for the segregation of different visual features, such as color, motion, and form, which are processed in specialized areas of the visual cortex.
Disorders and Clinical Implications
Disruptions to the connection between the optic nerves and the brain can result in various visual disorders and neurological conditions. Optic nerve damage, whether due to trauma, disease, or compression, can lead to vision loss or impairment. Conditions such as optic neuritis, glaucoma, and optic nerve hypoplasia are examples of disorders that affect the optic nerve and its function.
Furthermore, abnormalities in the development or connectivity of the optic nerves and visual pathways can manifest as congenital visual impairments or developmental disorders such as albinism or congenital nystagmus. Understanding the anatomy and function of the optic nerves is essential for diagnosing and treating these conditions effectively.
The connection between the optic nerves and the brain forms the foundation of human vision, allowing us to perceive and interact with the world around us. Through intricate pathways and complex neural processing, visual information is transmitted from the eyes to the brain, where it is interpreted and integrated to create our visual experience. By unraveling the mysteries of this connection, researchers and clinicians can gain valuable insights into the mechanisms of vision and develop novel strategies for diagnosing and treating visual disorders.


